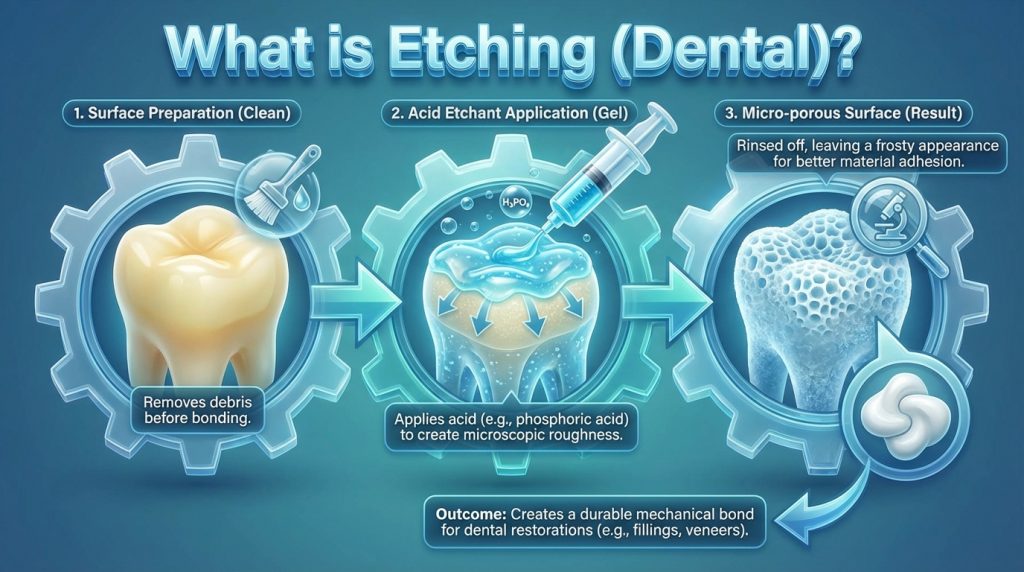
Etching (Dental)
Etching (Dental) is a controlled technique that applies a mild acidic gel—typically phosphoric acid—to the tooth surface to create microscopic pores in enamel or to modify the smear layer on dentine. By producing this micro-roughened surface, etching increases mechanical retention and promotes a stronger chemical bond between the tooth and restorative materials such as composite resin, veneers, crowns, inlays and sealants.
In practice the clinician places the etchant for a short, timed period, rinses and dries the tooth, then applies bonding agents and the chosen restorative material; the step usually adds only a few minutes to the overall procedure. Side effects are generally minimal but can include temporary sensitivity if dentine is exposed, and correct application and rinsing reduce risks; your dental professional will explain what to expect and any specific aftercare.
