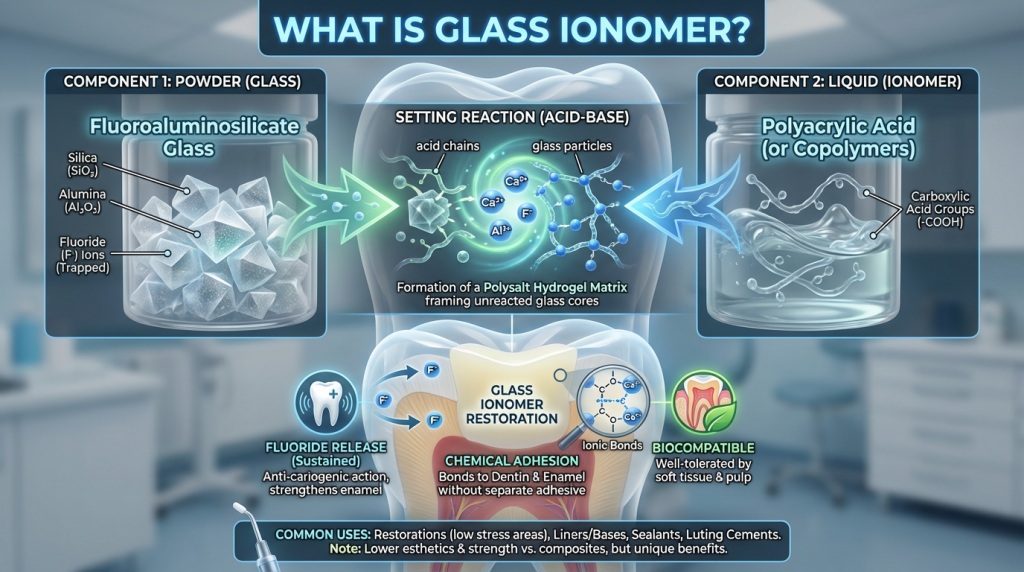
Glass Ionomer
Glass ionomer is a dental restorative material made from a silicate glass powder and an aqueous solution of polyacrylic acid which sets by an acid–base reaction. It bonds chemically to enamel and dentine without extensive tooth preparation, releases fluoride over time which can help reduce decay, and is commonly used for small fillings, cementation of crowns or bridges, liners or bases under other restorative materials, and for restorations in primary (baby) teeth.
Advantages of glass ionomer include its chemical adhesion to tooth tissues, relative tolerance to slight moisture during placement, and fluoride release, but it is generally less wear-resistant and less aesthetic than composite resins for large or high-stress restorations. Clinicians often use glass ionomer where moisture control is difficult, as a temporary or long-term solution in low-load areas, or as a liner beneath more durable restorations; replacement may be needed over time depending on wear and the location of the restoration.
