Gum Recession
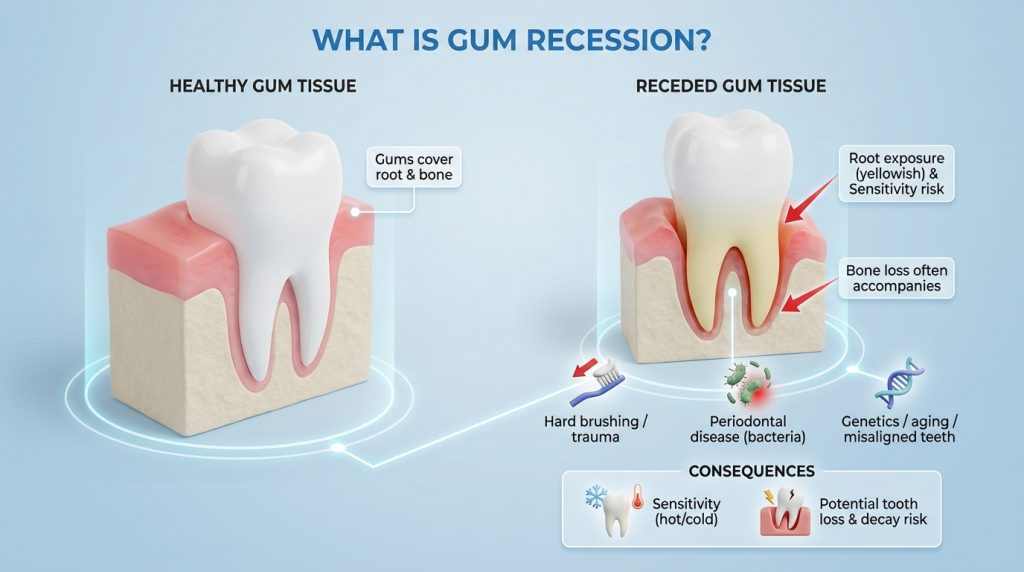
Gum recession is the gradual retreat of the gum margin away from the tooth, exposing the tooth root and creating the appearance of longer teeth. It can result from factors such as aggressive tooth brushing, periodontal (gum) disease, tobacco use, tooth grinding, misaligned teeth, or the natural ageing process, and commonly causes tooth sensitivity, visible root exposure and increased risk of root decay.
A dental professional diagnoses gum recession by examining the gums, measuring pocket depths and assessing root exposure, and management depends on severity: improving oral hygiene, treating gum disease, using desensitising agents or bonding to cover exposed root, and in more advanced cases surgical gum grafting to restore tissue. Preventive steps include gentle brushing with a soft-bristled brush, addressing gum inflammation early, avoiding tobacco, and regular dental check-ups to monitor and limit progression.
