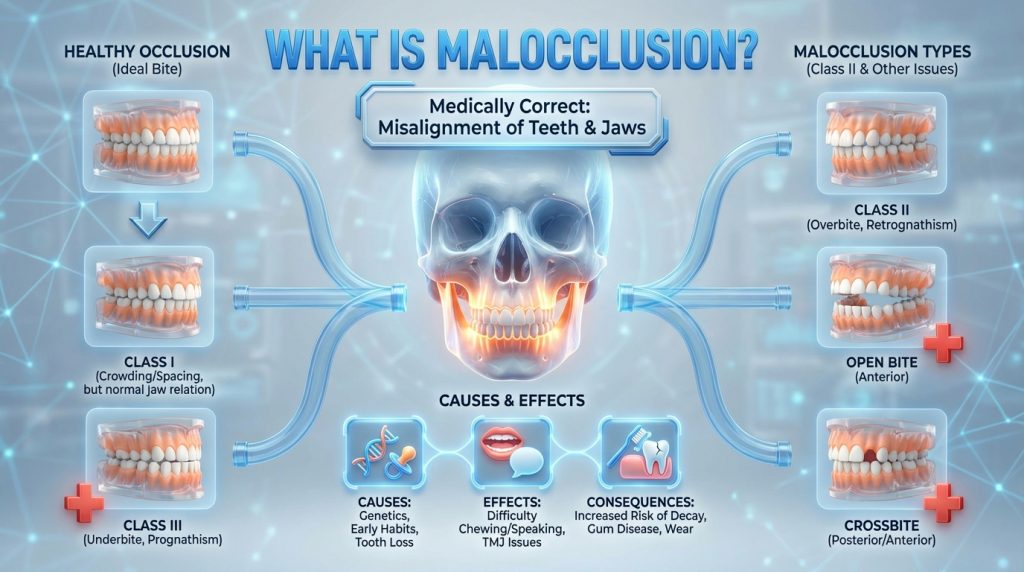
Malocclusion
Malocclusion describes an abnormal alignment of the teeth or a mismatch between the upper and lower jaws that affects the bite. It ranges from minor crowding or spacing to pronounced overbite, underbite, crossbite or open bite, and can result from genetic factors, differences in jaw growth, early loss of baby teeth, prolonged thumb-sucking or trauma; symptoms may include difficulty chewing, speech changes, uneven tooth wear, jaw pain and aesthetic concerns.
Diagnosis is made through a dental examination often supported by dental X-rays and study models, and management is tailored to the cause, severity and patient goals. Treatment options include orthodontic approaches such as braces or clear aligners, tooth extractions or growth modification in children, orthognathic (jaw) surgery for severe skeletal discrepancies, and restorative measures like veneers or crowns to improve function and appearance; an individualized plan focusing on function, comfort and oral health is important.
