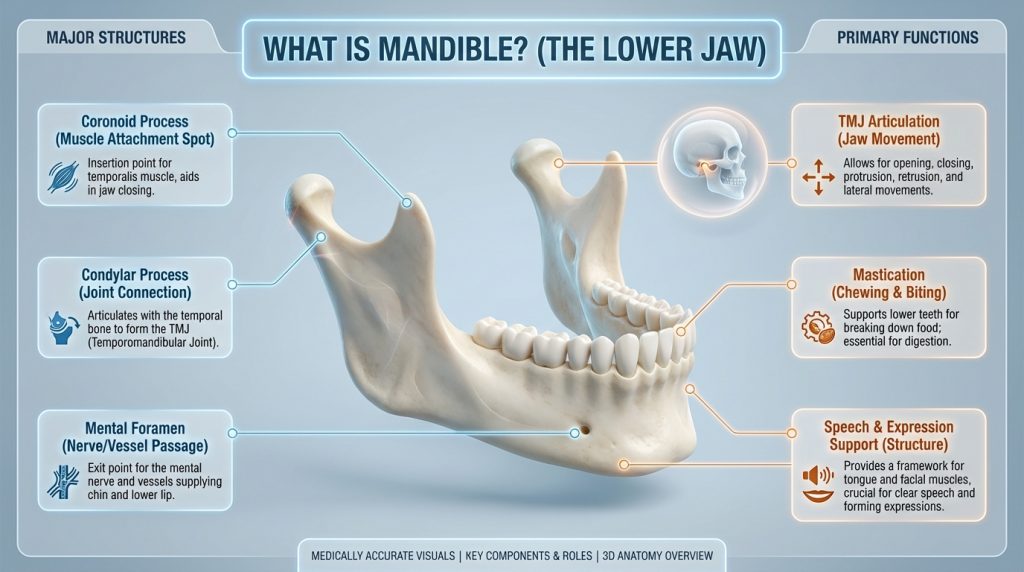
Mandible
The mandible, or lower jawbone, is the largest and strongest bone of the face and forms the movable lower part of the jaw. It supports the lower teeth along its alveolar ridge and consists of a horizontal body and two upward rami that terminate in processes and a condyle which articulate with the skull at the temporomandibular joints to enable chewing, speaking and facial movement.
Clinically the mandible is important for dental health and maxillofacial care because its shape, bone quality and joint function affect tooth alignment, bite (occlusion) and the planning of procedures such as extractions, implants or prosthetic replacement; it can also be affected by fractures, developmental differences, infections and temporomandibular disorders, which are evaluated using clinical examination and imaging.
