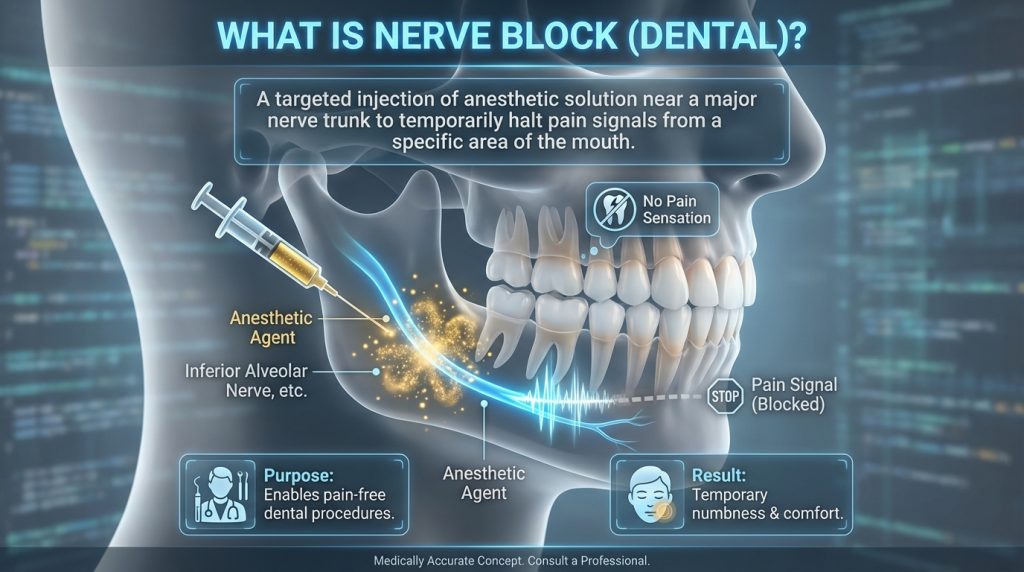
Nerve Block (Dental)
A Nerve Block (Dental) is a form of local anaesthesia in which an anaesthetic drug is injected close to a specific nerve to block sensation from a larger region of the mouth or jaw. Commonly targeted nerves include the inferior alveolar nerve for lower-jaw procedures and branches of the maxillary nerve for upper-jaw work, and the technique is chosen when deeper or wider-ranging numbness is required compared with topical or infiltration anaesthesia.
Nerve blocks provide effective pain control for procedures such as extractions, implant placement and root canal treatment and typically cause numbness that can last for several hours. Side effects are usually temporary and can include tingling, drooping of nearby muscles or bruising at the injection site; rare complications include prolonged numbness or nerve injury, so clinicians take care with technique and patients are advised to avoid chewing until normal sensation returns and to report any persistent symptoms.
