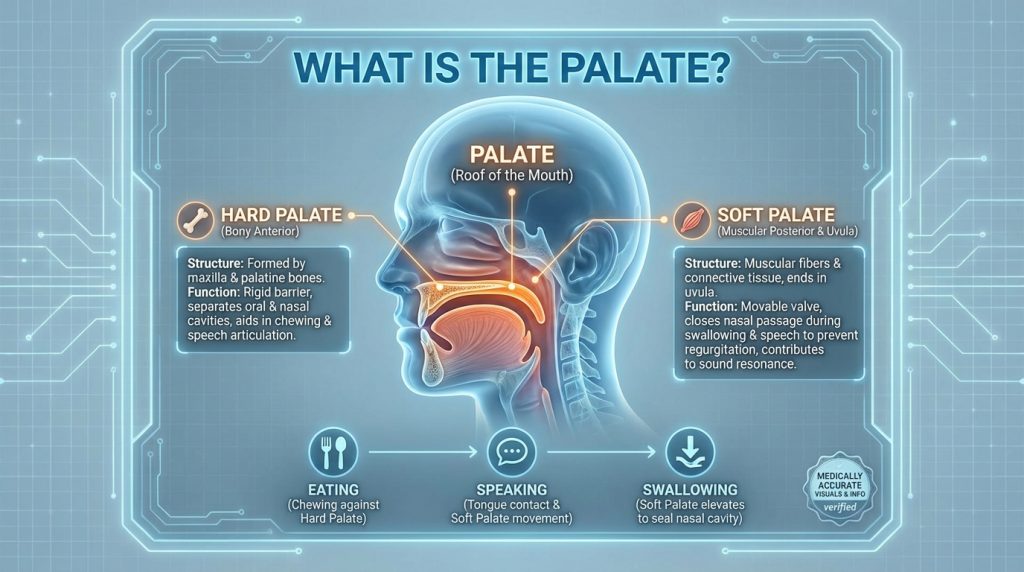
Palate
The palate is the roof of the mouth, composed of an anterior hard palate made of bone and a posterior soft palate made of muscle and connective tissue. This structure separates the oral and nasal cavities and contributes to speech articulation, swallowing by guiding food and liquid, and the ability to form suction for denture retention.
From a clinical perspective, the palate is assessed for developmental conditions such as cleft palate, for anatomical variations like palatal tori (bony prominences), and for signs of infection, ulcers or lesions. Its shape and health influence dental procedures and prosthetic design, so dentists examine the palate as part of routine oral assessments to identify local problems or indicators of systemic disease.
