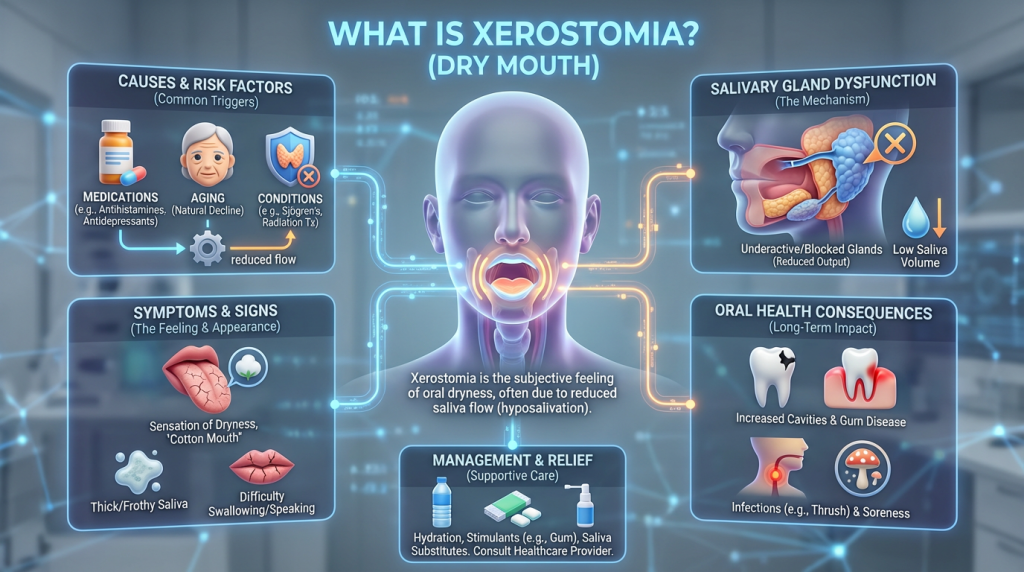
Xerostomia
Xerostomia, commonly known as dry mouth, is a symptom resulting from reduced or absent saliva production. People with xerostomia may notice a persistent dry or sticky feeling in the mouth, altered taste, difficulty chewing or swallowing, a sore or burning tongue, cracked lips, or an increase in dental cavities and oral infections; it can result from medications, radiation therapy to the head and neck, systemic conditions (such as Sjogren’s syndrome or diabetes), dehydration, or nerve damage.
Management focuses on relieving symptoms and reducing oral health risks and may include frequent sips of water, saliva substitutes or stimulants (like sugar-free chewing gum or lozenges) when appropriate, improving oral hygiene, topical fluoride to help protect teeth, and reviewing medications or medical causes with a healthcare professional. Regular dental check-ups are important because reduced saliva impairs the mouth’s natural ability to neutralise acids and control bacteria, raising the chance of decay and gum disease.
