Bone Graft
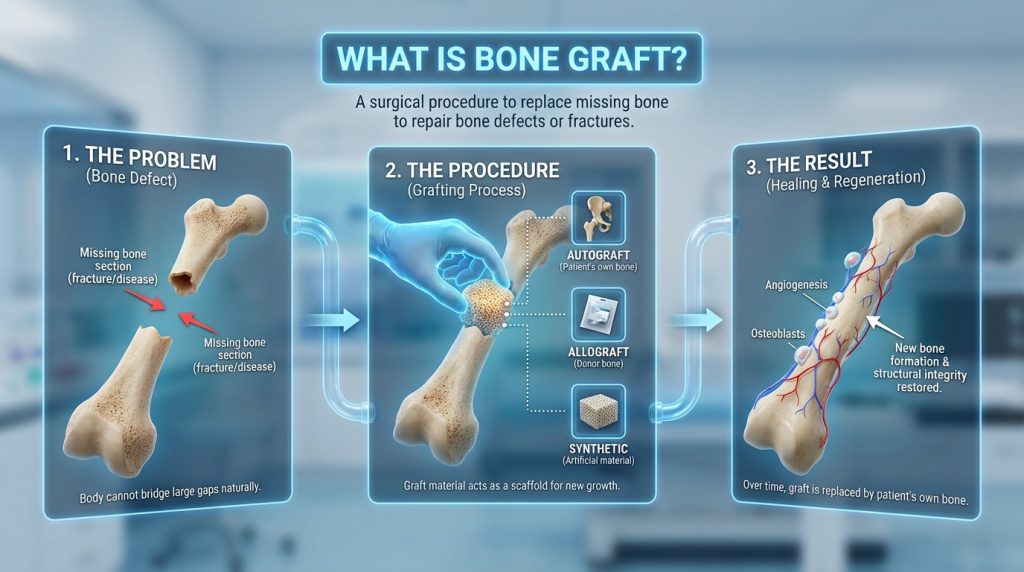
A bone graft is a surgical procedure used to rebuild or augment missing or deficient bone in the jaw. It provides additional bone volume and structural support when natural bone has been lost due to tooth extraction, periodontal disease, trauma, infection, or long-term resorption, and it is commonly used to create a stable foundation for dental implants or to restore facial contours.
Grafting options include using the patient’s own bone (autograft), donor bone (allograft), animal-derived materials (xenograft), or synthetic substitutes, and the choice depends on the size of the defect, treatment goals, and overall health. The procedure is usually performed under local or general anaesthesia, requires a healing period of weeks to months for the graft to integrate, and carries risks such as infection, rejection or partial graft failure, so careful assessment and follow-up are important.
