Dental Pulp
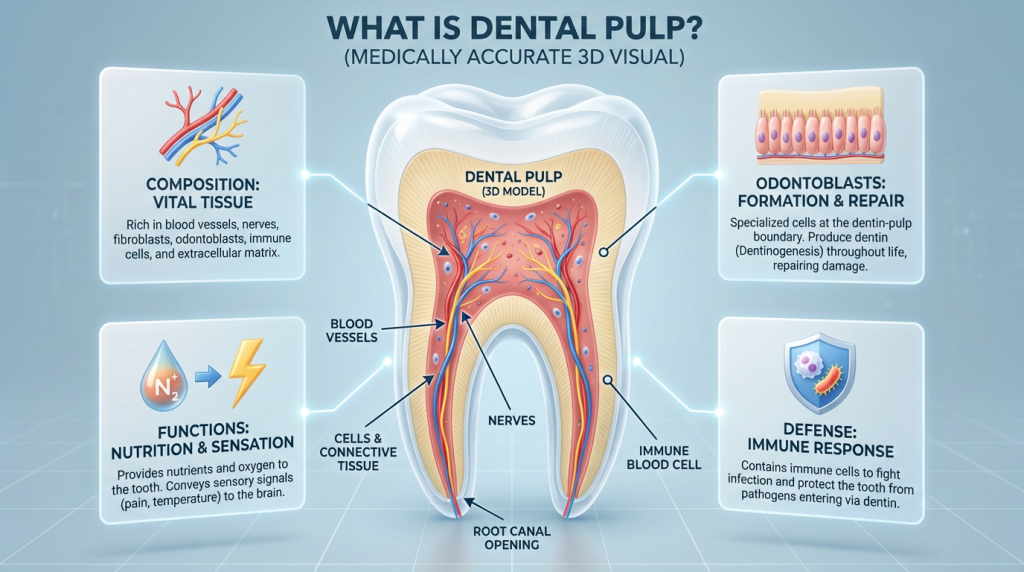
The dental pulp is the soft tissue at the centre of a tooth that contains nerves, blood vessels and connective tissue. It nourishes the tooth, transmits sensory signals such as pain and temperature, and plays a role in forming dentine during tooth development.
When the pulp becomes inflamed or infected due to deep decay, trauma or repeated dental work, symptoms can include persistent toothache, sensitivity to hot or cold and swelling. Dentists diagnose pulp problems with clinical tests and X-rays and treat them by removing diseased pulp and sealing the root canal system (root canal treatment) to preserve the tooth when possible, or by extracting the tooth and replacing it with a dental implant if necessary.
